Article contributors: Bhaskar Ray, Fred Raddatz, Shangmin Lin
AMIDST the excitement of new energy sources, the reliability of our energy infrastructure cannot be overlooked. Black start services emerge as a pivotal solution that will bridge the gap between ambition and dependability.
Alongside black start services, energy storage systems (ESS) are becoming increasingly important in the energy industry. These systems can be co-located with other energy sources like solar projects. They can also be standalone systems like the Qcells built Cunningham project.
BESS provides a lot of opportunities in terms of transmission. Energy storage supports transmission needs by increasing transfer capability and providing stability services via voltage control and inertia. Amy Jo explains these benefits in her post Storage as a Transmission Only Asset.
In addition to BESS, grid-forming inverter (GFI) projects offer another dimension to the reliability and financial potential of renewable energy integration.
What Are Grid-Forming Inverters?
Traditional power grids rely on the stability of large generators. As we move towards renewables, grid-following inverters need that existing grid signal to function. GFIs break this dependency. Besides providing system reliability benefits to the power system GFI projects are also eligible to be more financially compensated compared to traditional grid following inverter projects.
GFI projects can participate in energy markets and capacity markets similar to grid following projects, to make financial profit from energy arbitrage and providing load serving capacity.
Additionally, GFI projects are entitled to receive more revenue than grid following projects in ancillary service markets by serving as a black start resource to help restoration and re-energization of grid to system frequency and come online after suffering from a blackout or islanding event due to unforeseen transmission disturbances.
Understanding The Demand for Black Start Services
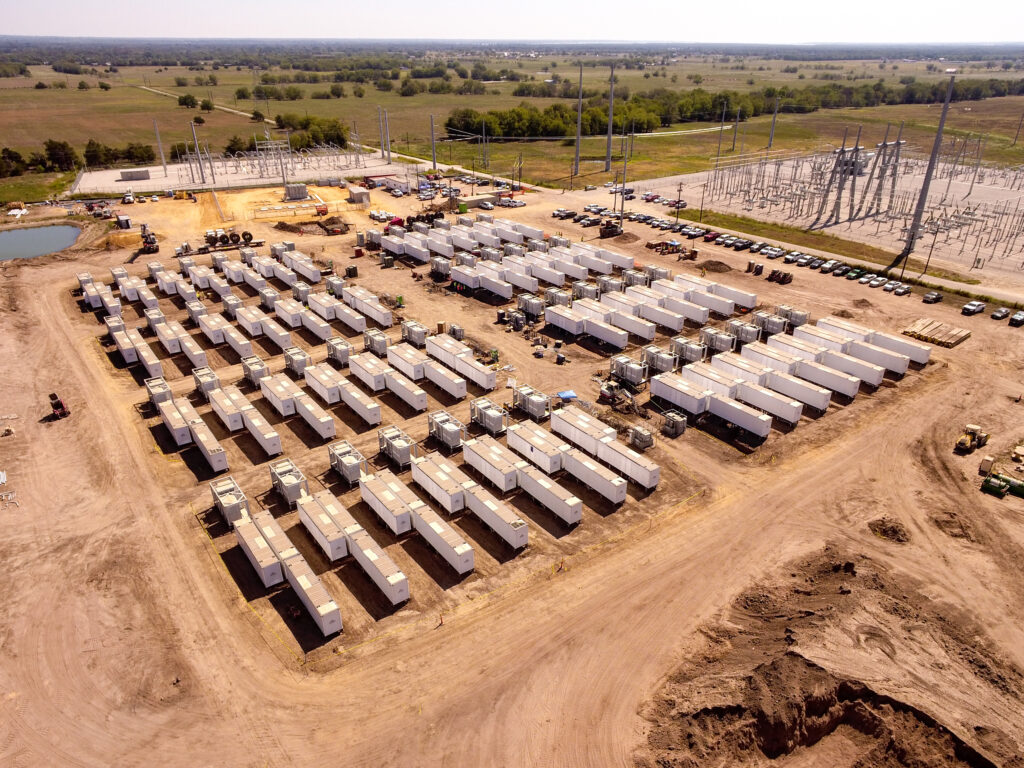

In an extreme event which causes system-wide blackout, black start services are used to re-energize the transmission system and provide power to start other generators that cannot self-start and synchronize to system frequency. Independent System Operator / Regional Transmission Organizations (ISO/RTOs) require black start services in specific regions of their system to ensure that they will have adequate start power to bring other generators online and eventually bring the whole system back online. ISO/RTOs typically publish a request for proposal (RFP) to acquire black start service and pay the black start resource annually if they pass the ISO/RTO defined tests to prove their capability for black start capabilities.
Unlike grid following battery energy storage system (BESS) units, GFI BESS units can control the inverter voltage magnitude, frequency, and angle and maintain stable operation under very low grid strength, which makes them qualified of providing black start service. And since the current black start resources are primarily natural gas plants, which are more likely to be retired in the future, ISO/RTOs will need to seek black start units from new technologies like energy storage.
Since ISO/RTOs draw individual contracts with black start resource units, there is no “clearing price.” Black start compensation/revenue is a non-public information. However, this revenue is addictive to other market revenues. If a unit is selected as a black start resource, it can still participate in energy markets, ancillary service markets, and capacity markets just like any other unit without restriction.
Implementation of BESS Black Start Systems

In California, Siemens has also announced that it will build a battery energy storage system for the Marsh Landing Generation Station to provide black start capabilities.
Another example from California, Pacific Gas and Electric Company and Energy Vault Holding have also partnered to deploy a utility-scale battery plus green hydrogen long-duration energy storage system. The system’s hybrid architecture with grid formation will have black start capability and can operate as microgrid to keep Calistoga and its surrounding area running for at least 48 hours during a system-wide blackout.
In Indiana, FlexGen 112 MVA generating step‐up transformer (GSU) was black started by an energy storage system.




 USA & Canada
USA & Canada Korea
Korea Germany
Germany United Kingdom
United Kingdom France
France Italy
Italy Netherlands
Netherlands Greece
Greece Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Hungary
Hungary Spain
Spain Japan
Japan